Distal radial artery in endovascular interventions - Scientific Figure on ResearchGate. Available from: https://www.researchgate.net/figure/Radial-artery-catheterization-at-the-dorsum-of-hand-our-observation_fig8_319162208 [accessed 13 Jun, 2023]
The radial artery has become the preferred access point for interventional cardiology procedures in most hospitals because it is associated with less bleeding complications and faster patient recovery. However, there are cases when the radial artery needs to be preserved like when the patient will likely need a conduit for dialysis or for coronary artery bypass surgery. Recent studies have looked into whether distal radial access maybe a safe alternative to the conventional radial artery approach.
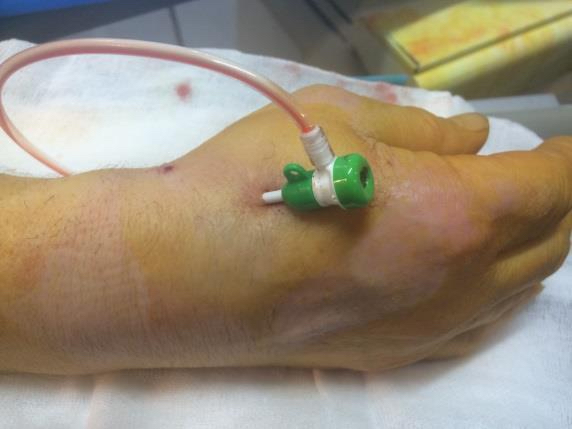
Distal transradial access (dTRA) was first published in 2017 and was followed shortly after by numerous studies looking into the safety and effectiveness of this new technique. In conventional transradial approach (TRA), the access point is on the inside of the forearm above the wrist. In dTRA, also referred to as snuffbox approach, the entry point is on the triangular depression on the back of the hand - just below the thumb.
There are potential advantages of using dTRA instead of the conventional TRA. First, there is a lower risk of radial artery occlusion (RAO) as there are alternate blood flow routes at the wrist. There is also no need for additional equipment to support the patient's arm during the procedure as dTRA has the hand in its natural resting position making it more comfortable for patients. Furthermore, because dTRA is more superficial and does not impede wrist movement, it is quicker to achieve hemostasis during recovery.
However, there are limitations specific to using dTRA. Aside from the learning curve and device size restrictions due to the smaller diameter of the distal radial artery, it is also closer to the radial nerve which increases the risk of hand function complications.
The Distal vs Proximal Radial Artery (DIPRA) study compared hand functions like hand-grip strength, pinch strength and patient perception in 300 patients between the two approaches. The 1-year results were presented at the Society for Cardiovascular Angiography and Interventions (SCAI) 2023 Scientific Sessions last month. The DIPRA study showed no significant difference in hand function between conventional TRA and dTRA. It is also worth noting that the research was not restricted to doctors well-experienced in dTRA which reflects real-world practices.
While further research is still needed to confirm the clinical benefits of dTRA before its adoption to procedural guidelines, this new technique opens up more options for doctors and patients alike.
References:
1. Al-Azizi, K., Idris, A., Christensen, J. D., Hamandi, M., Hale, S. E., Martits-Chalangari, K., Van Zyl, J. S., Ravindranathan, P., Banwait, J. K., Mcckracken, J., Smith, A., Apakama, G. P., Swim, J., Dolton, P., Chionh, K., DiMaio, M. A., Thomas, S., Szerlip, M., Sayfo, S., . . . Potluri, S. (2022). Distal Versus Proximal Radial Artery Access for Cardiac Catheterization and Intervention: Design and Rationale of the DIPRA Trial. Cardiovascular Revascularization Medicine, 35, 104–109. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carrev.2021.04.001
2. Sgueglia, G. A., Di Giorgio, A., Gaspardone, A., & Babunashvili, A. (2018). Anatomic Basis and Physiological Rationale of Distal Radial Artery Access for Percutaneous Coronary and Endovascular Procedures. Jacc-cardiovascular Interventions, 11(20), 2113–2119. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcin.2018.04.045
3. Kaledin, Aleksandr & Kochanov, In & Podmetin, Ps & Seletsky, Ss & Ardeev, Vn. (2017). Distal radial artery in endovascular interventions. 10.13140/RG.2.2.13406.33600.
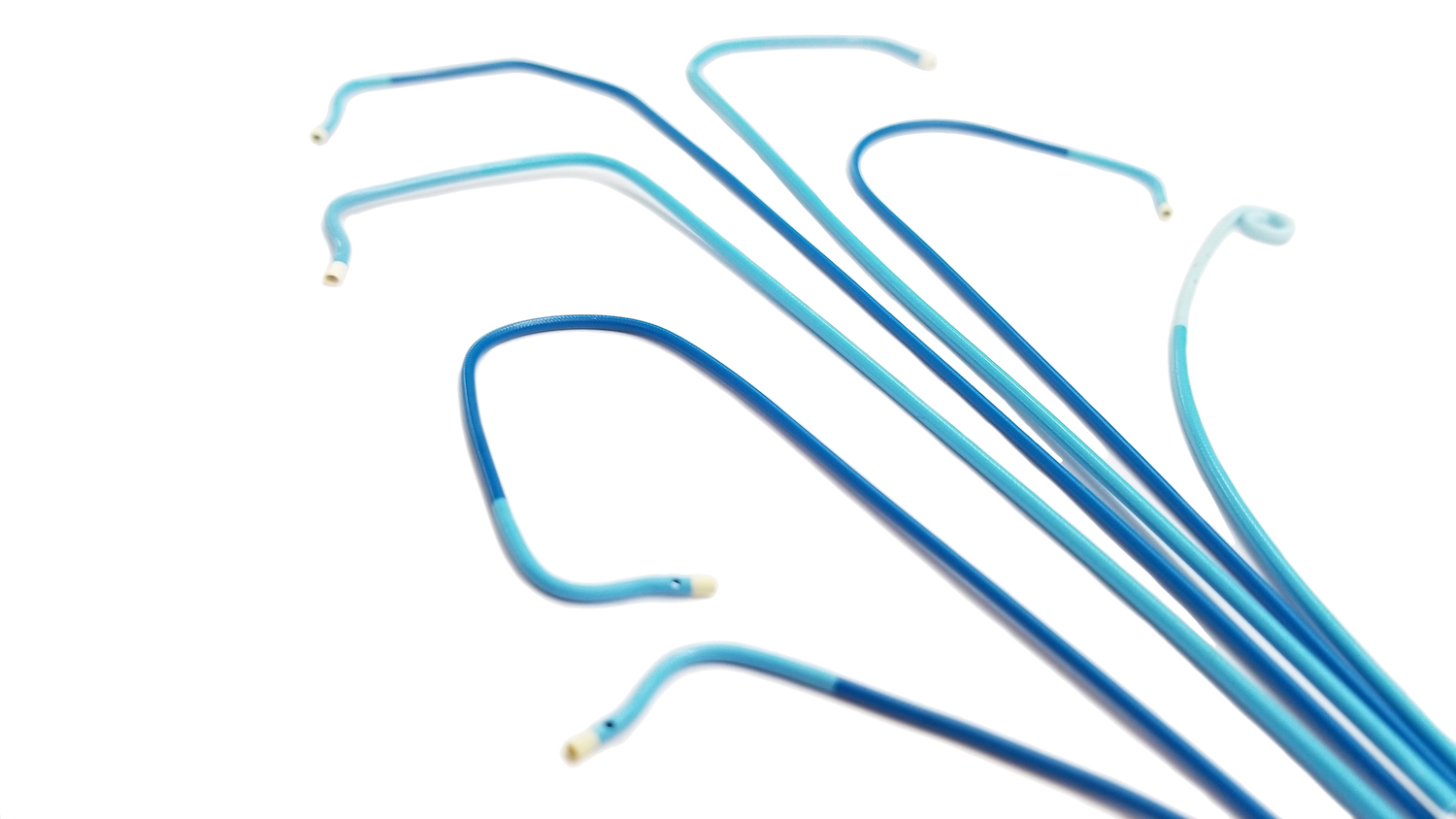

The distal radial artery access point is about 5cm lower than the conventional TRA site which makes standard 100cm catheters a bit too short to properly engage the coronary arteries, especially in taller patients. Technowood SoftNAV catheters have 105cm effective length to allow for some leeway for doctors to smoothly perform procedures even in distal transradial approach.
Not all products shown are approved for sale in all countries.
Please contact the regional Technowood representative for more information.